OpenShift
This documentation provides guidance on installing the MariaDB Enterprise Operator operator in OpenShift. This operator has been certified by Red Hat and it is available in the OpenShift console.
Operators are deployed into OpenShift with the Operator Lifecycle Manager (OLM), which facilitates the installation, updates, and overall management of their lifecycle.
Table of contents
- Prerequisites
PackageManifestSecurityContextConstraints- Installation in all namespaces
- Installation in specific namespaces
- Release channels
- Updates
- Uninstalling
- OpenShift console
Prerequisites
Configure your customer credentials as described in the documentation to be able to pull images.
The recommended way to configure credentials is to use the global pull secret provided by OpenShift, as described in this section. Alternatively, the operator bundle has a mariadb-enterprise imagePullSecret configured by default. This means that you can configure a Secret named mariadb-enterprise in same namespace where the operator will be installed in order to pull images from the MariaDB Enterprise registry.
PackageManifest
You can install the certified operator in OpenShift clusters that have the mariadb-enterprise-operator packagemanifest available. In order to check this, run the following command:
oc get packagemanifests -n openshift-marketplace mariadb-enterprise-operator NAME CATALOG AGE mariadb-enterprise-operator Certified Operators 21h
SecurityContextConstraints
Both the operator and the operand Pods run with the restricted-v2 SecurityContextConstraint, the most restrictive SCC in OpenShift in terms of container permissions. This implies that OpenShift automatically assigns a SecurityContext for the Pods with minimum permissions, for example:
securityContext: allowPrivilegeEscalation: false capabilities: drop: - ALL runAsNonRoot: true runAsUser: 1000650000
IMPORTANT
OpenShift does not assignSecurityContextsin thedefaultandkube-systemnamespaces. Please refrain from deploying operands on them, as it will result in permission errors when trying to write to the filesystem.
You can read more about SecurityContextConstraints in the OpenShift documentation.
Installation in all namespaces
To install the operator watching resources on all namespaces, you need to to create a Subscription object for mariadb-enterprise-operator using the stable channel in the openshift-operators namespace:
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1 kind: Subscription metadata: name: mariadb-enterprise-operator namespace: openshift-operators spec: channel: stable installPlanApproval: Automatic name: mariadb-enterprise-operator source: certified-operators sourceNamespace: openshift-marketplace startingCSV: mariadb-enterprise-operator.v1.0.0
This will use the global-operators OperatorGroup that is created by default in the openshift-operators namespace. This OperatorGroup will watch all namespaces in the cluster, and the operator will be able to manage resources across all namespaces.
You can read more about OperatorGroups in the OpenShift documentation.
Installation in specific namespaces
In order to define which namespaces the operator will be watching, you need to create an OperatorGroup in the namespace where the operator will be installed:
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1 kind: OperatorGroup metadata: name: mariadb-enterprise-operator namespace: my-namespace spec: targetNamespaces: - my-namespace - my-other-namespace - my-other-other-namespace upgradeStrategy: Default
This OperatorGroup will watch the namespaces defined in the targetNamespaces field. The operator will be able to manage resources only in these namespaces.
Then, the operator can be installed by creating a Subscription object in the same namespace as the OperatorGroup:
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1 kind: Subscription metadata: name: mariadb-enterprise-operator namespace: my-namespace spec: channel: stable installPlanApproval: Automatic name: mariadb-enterprise-operator source: certified-operators sourceNamespace: openshift-marketplace startingCSV: mariadb-enterprise-operator.v1.0.0
Release channels
Currently, the only release channel available to install the operator is stable, which contains supported releases of the operator. This is controlled by the channel field in the Subscription object.
Updates
Updates are fully managed by OLM and controlled by the installPlanApproval field in the Subscription object. The default value is Automatic, which means that OLM will automatically update the operator to the latest version available in the channel. If you want to control the updates, you can set this field to Manual, and OLM will only update the operator when you approve the update.
Uninstalling
The first step for uninstalling the operator is to delete the Subscription object. This will not remove the operator, but it will stop OLM from managing the operator:
oc delete subscription mariadb-enterprise-operator
After that, you can uninstall the ClusterServiceVersion (CSV) object that was created by OLM. This will remove the operator from the cluster:
oc delete clusterserviceversion mariadb-enterprise-operator.v1.0.0
OpenShift console
As an alternative to create Subscription objects via the command line, you can install operators by using the OpenShift console. Go to the Operators > OperatorHub section and search by mariadb enterprise:
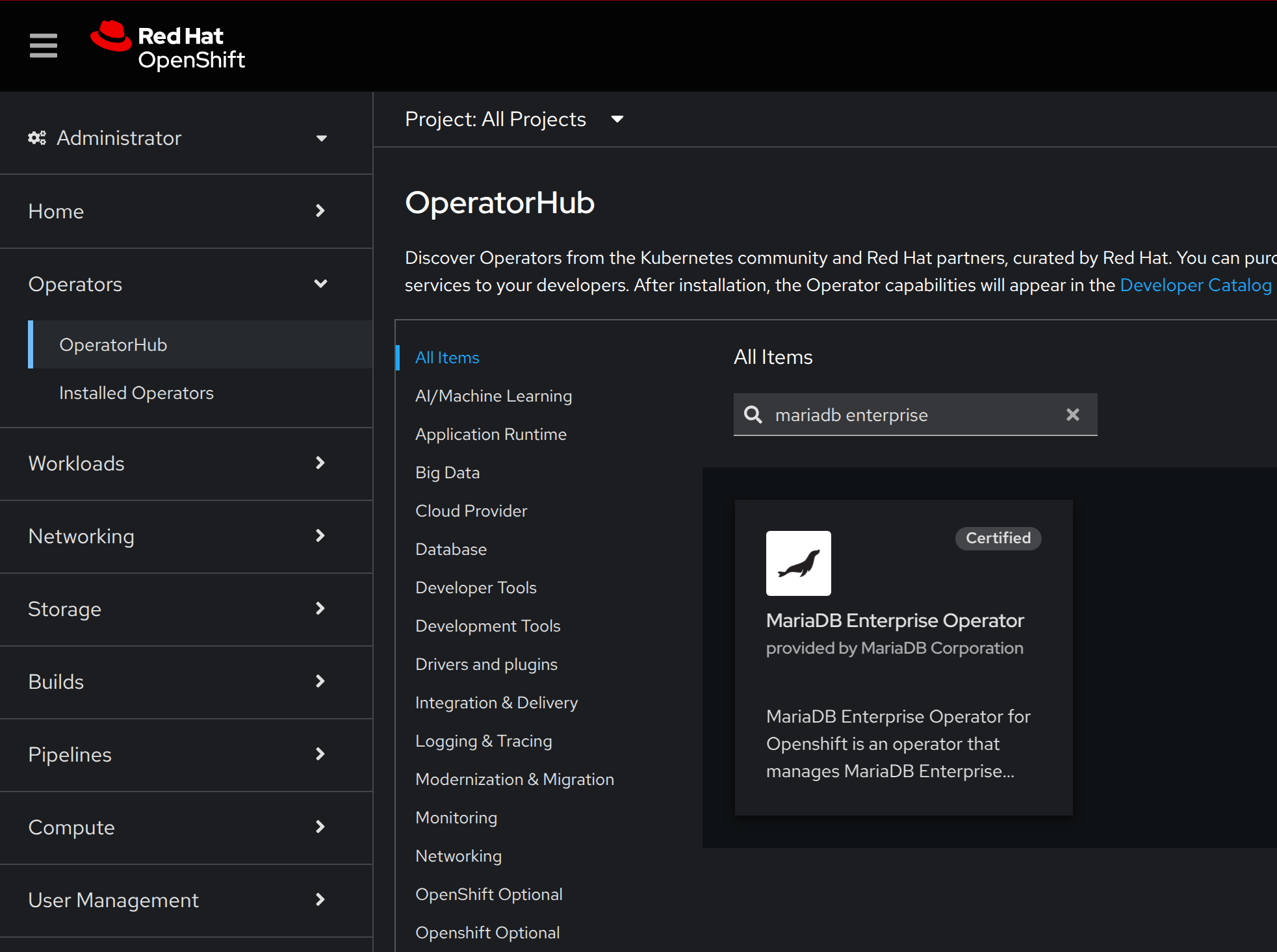
Select MariaDB Enterprise Operator, click on install, and you will be able to create a Subscription object via the UI.
Once deployed, the operator comes with example resources that can be deployed from the console directly. For instance, to create a MariaDB:
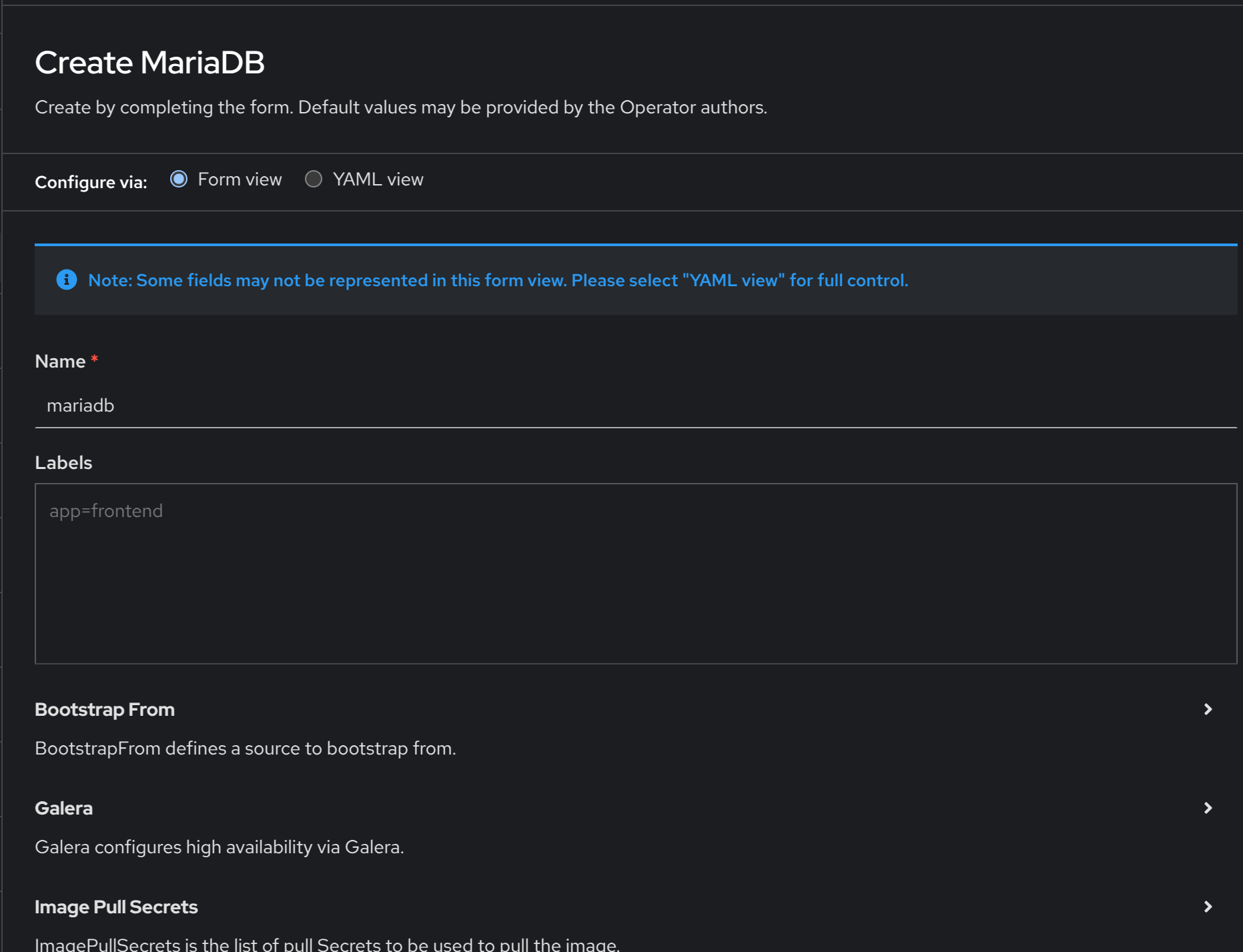
As you can see in the previous screenshot, the form view that the OpenShift console offers is limited, we recommend using the YAML view: