Using MaxGUI Tutorial
Using MaxGUI Tutorial
Introduction
This tutorial is an overview of what the MaxGUI offers as an alternative solution to MaxCtrl.
Dashboard
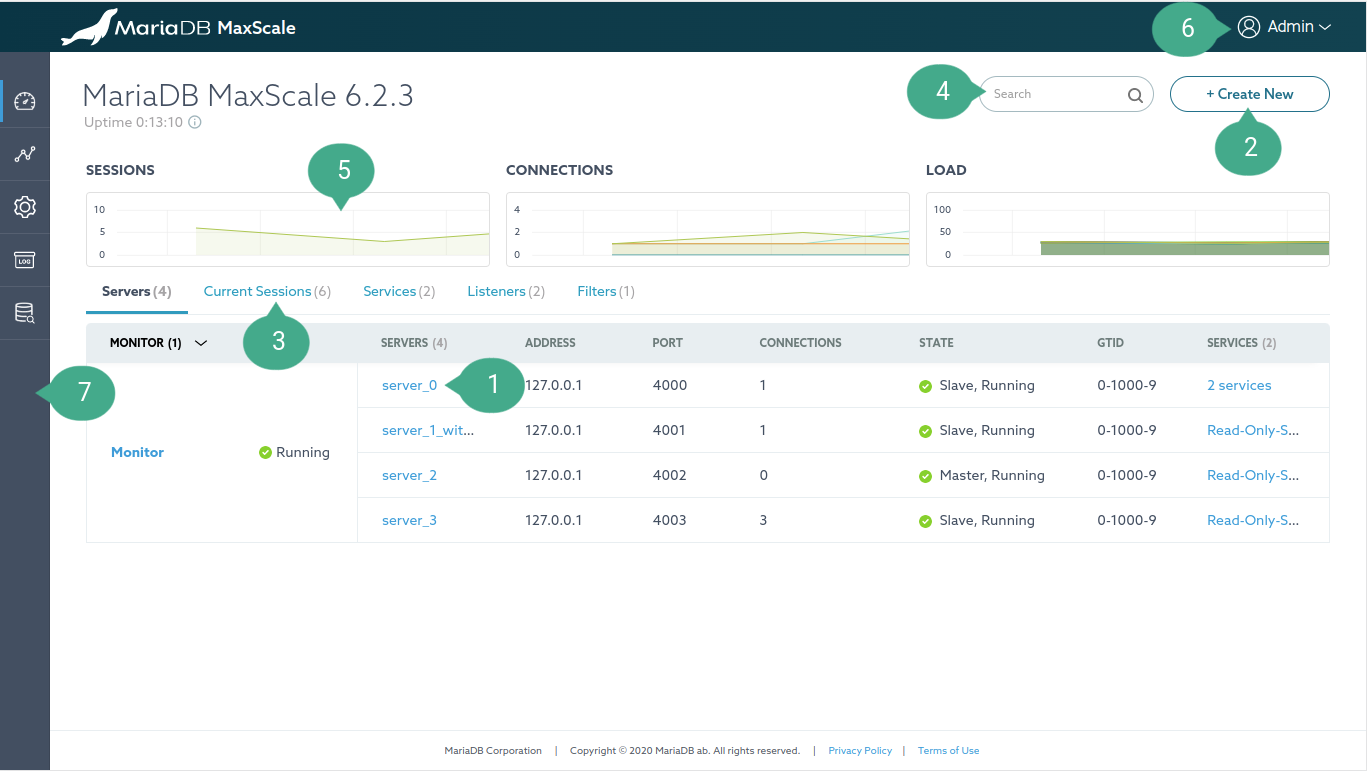
Annotation
- MaxScale object. i.e. Service, Server, Monitor, Filter, and Listener (Clicking on it will navigate to its detail page)
- Create a new MaxScale object.
- Dashboard Tab Navigation.
- Search Input. This can be used as a quick way to search for a keyword in tables.
- Dashboard graphs. Refresh interval is 10 seconds.
- SESSIONS graph illustrates the total number of current sessions.
- CONNECTIONS graph shows servers current connections.
- LOAD graph shows the last second load of thread.
- Logout of the app.
- Sidebar navigation menu. Access to the following pages: Dashboard, Visualization, Settings, Logs Archive, Query Editor
Create a new MaxScale object
Clicking on the Create New button (Annotation 2) to open a dialog for creating a new object.
View Replication Status
The replication status of a server monitored by MariaDB-Monitor can be viewed by mousing over the server name. A tooltip will be displayed with the following information: replication_state, seconds_behind_master, slave_io_running, slave_sql_running.
Detail
This page shows information on each MaxScale object and allow to edit its parameter, relationships and perform other manipulation operations. Most of the control buttons will be shown on the mouseover event. Below is a screenshot of a Monitor Detail page, other Detail pages also have a similar layout structure so this is used for illustration purpose.
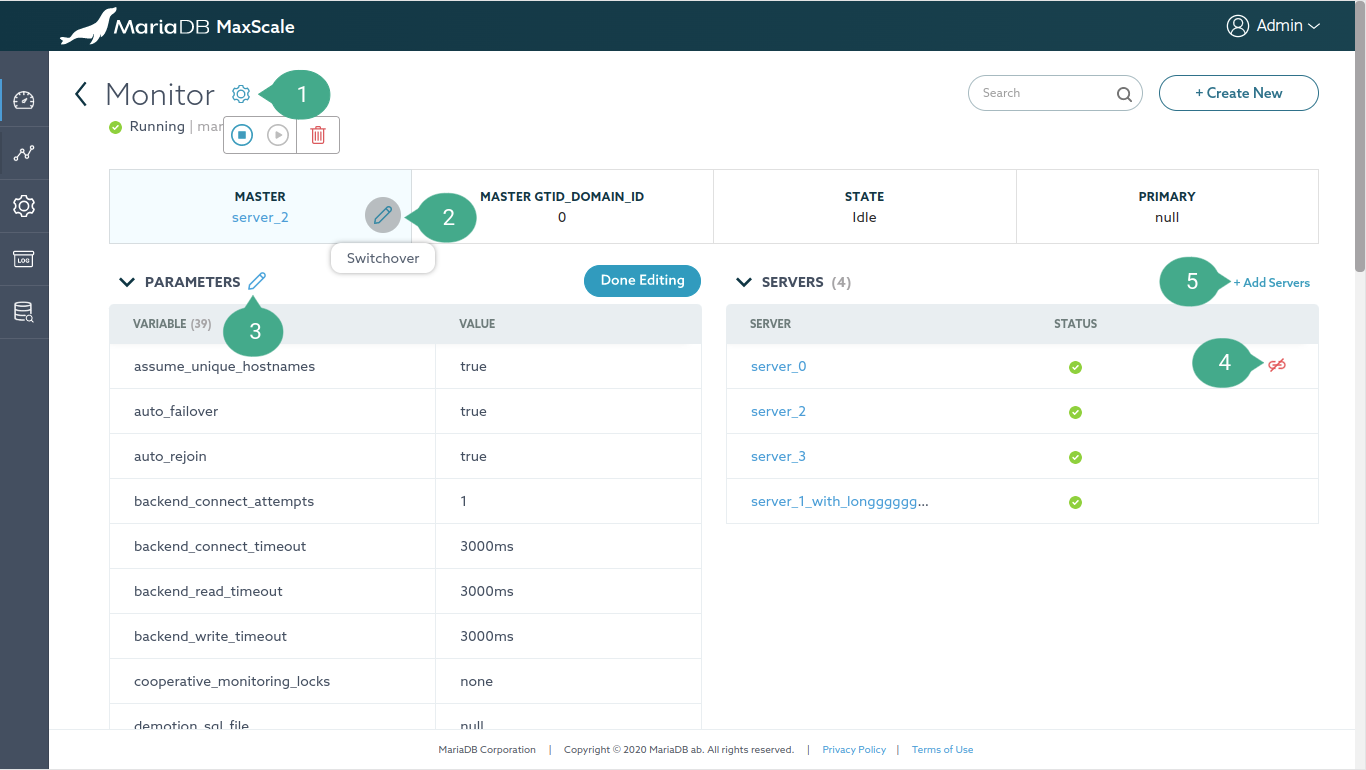
Annotation
- Settings option. Clicking on the gear icon will show icons allowing to do
different operations depending on the type of the Detail page.
- Monitor Detail page, there are icons to Stop, Start, and Destroy monitor.
- Service Detail page, there are icons to Stop, Start, and Destroy service.
- Server Detail page, there are icons to Set maintenance mode, Clear server state, Drain and Delete server.
- Filter and Listener Detail page, there is a delete icon to delete the object.
- Switchover button. This button is shown on the mouseover event allowing to swap the running primary server with a designated secondary server.
- Edit parameters button. This button is shown on the mouseover event allowing to edit the MaxScale object's parameter. Clicking on it will enable editable mode on the table. After finishing editing the parameters, simply click the Done Editing button.
- A Detail page has tables showing "Relationship" between other MaxScale object. This "unlink" icon is shown on the mouseover event allowing to remove the relationship between two objects.
- This button is used to link other MaxScale objects to the relationship.
Visualization
This page visualizes MaxScale configuration and clusters.
Configuration
This page visualizes MaxScale configuration as shown in the figure below.
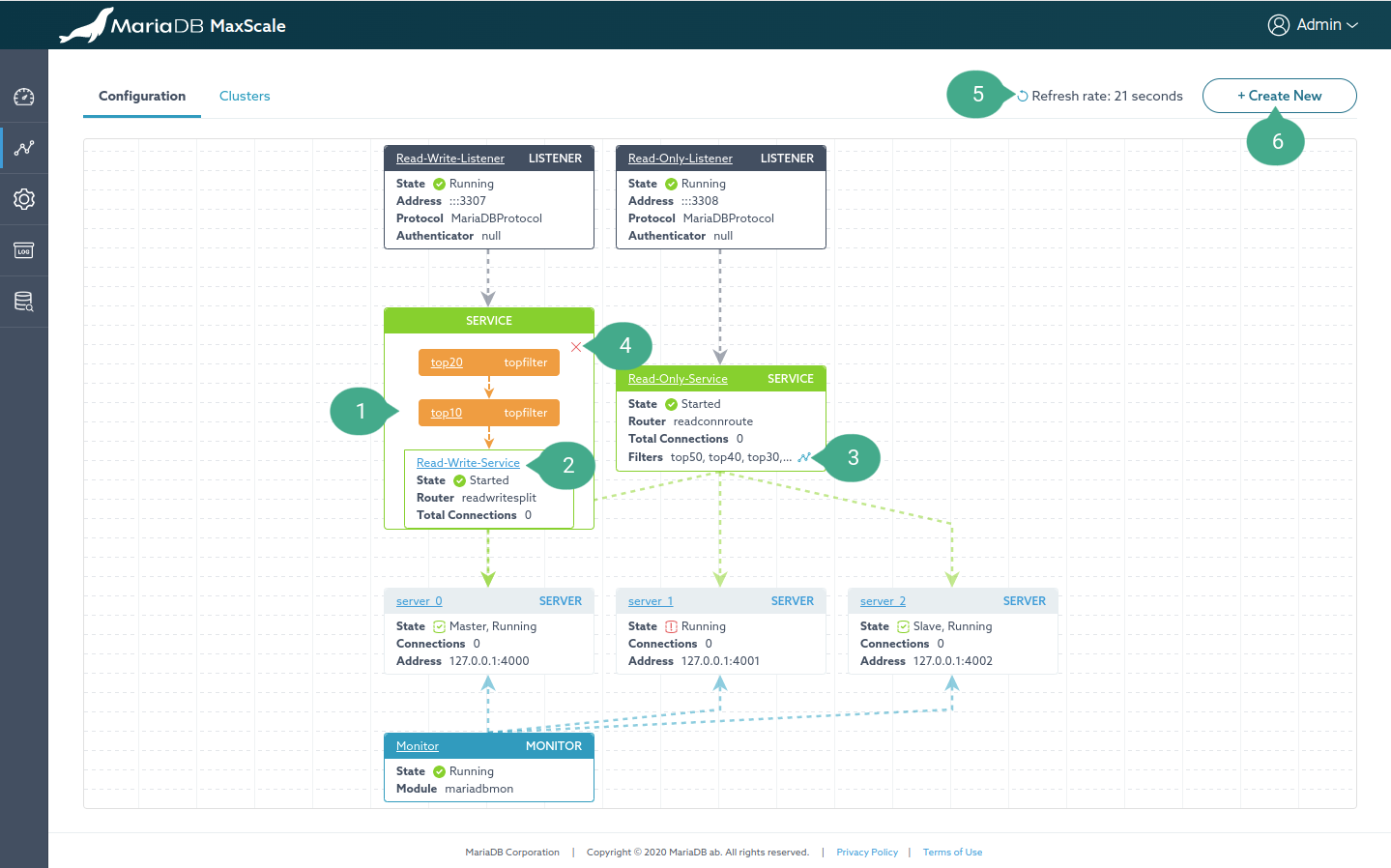
Annotation
- A MaxScale object (a node graph). The position of the node in the graph can be changed by dragging and dropping it.
- Anchor link. The detail page of each MaxScale object can be accessed by clicking on the name of the node.
- Filter visualization button. By default, if the number of filters used by a service is larger than 3, filter nodes aren't visualized as shown in the figure. Clicking this button will visualize them.
- Hide filter visualization button.
- Refresh rate dropdown. The frequency with which the data is refreshed.
- Create a new MaxScale object button.
Clusters
This page shows all monitor clusters using mariadbmon module in a card-like view. Clicking on the card will visualize the cluster into a tree graph as shown in the figure below.
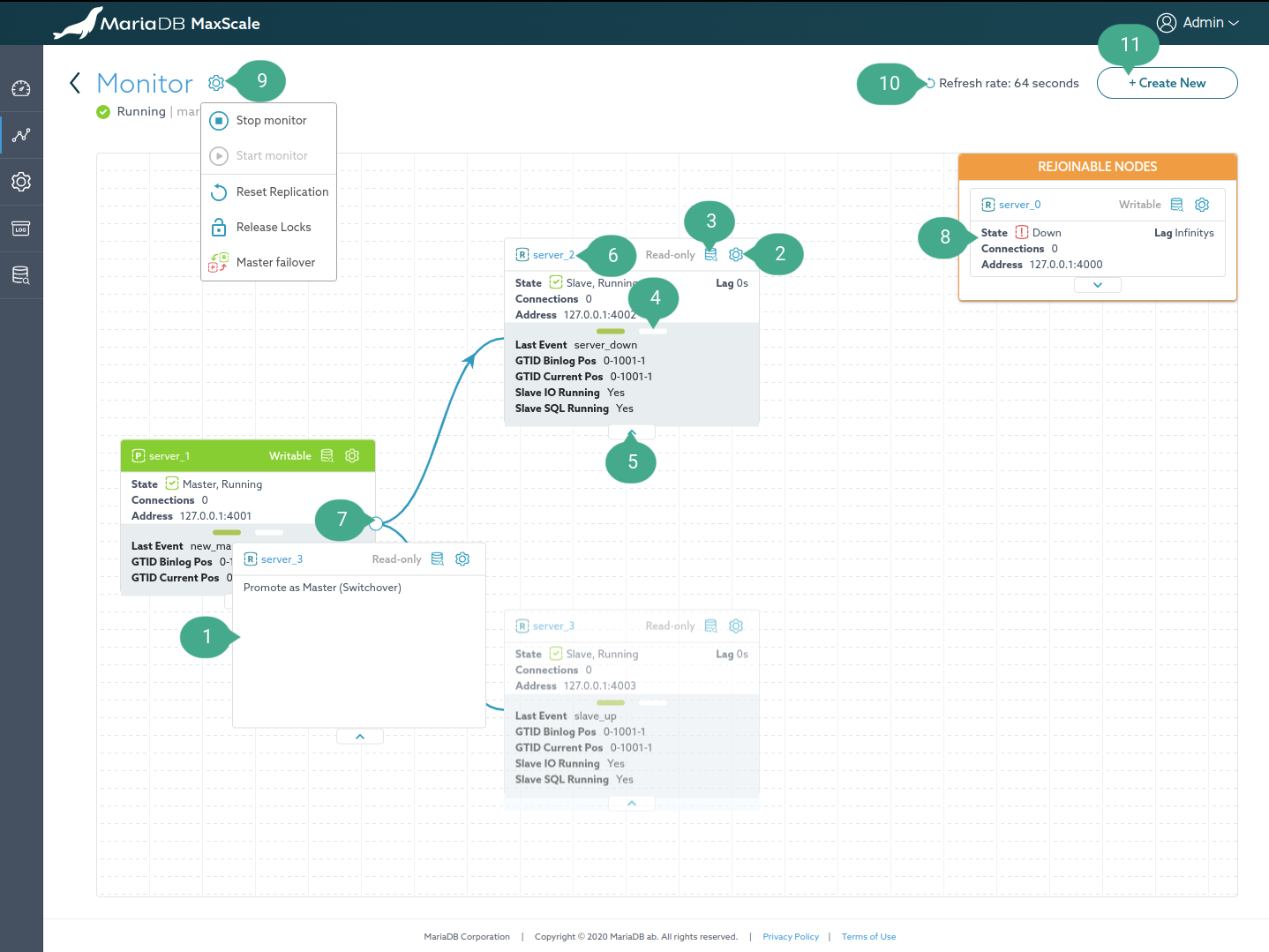
Annotation
- Drag a secondary server on top of a primary server to promote the secondary server as the new primary server.
- Server manipulation operations button. Showing a dropdown with the following
operations:
- Set maintenance mode: Setting a server to a maintenance mode.
- Clear server state: Clear current server state.
- Drain server: Drain the server of connections.
- Quick access to query editor button. Opening the
Query Editorpage for this server. If the connection is already created for that server, it'll use it. Otherwise, it creates a blank worksheet and shows a connection dialog to connect to that server. - Carousel navigation button. Viewing more information about the server in the next slide.
- Collapse the carousel.
- Anchor link of the server. Opening the detail page of the server in a new tab.
- Collapse its children nodes.
- Rejoin node. When the
auto_rejoinparameter is disabled, the node can be manually rejoined by dragging it on top of the primary server. - Monitor manipulation operations button. Showing a dropdown with the
following operations:
- Stop monitor.
- Start monitor.
- Reset Replication.
- Release Locks.
- Master failover. Manually performing a master failover. This option is
visible only when the
auto_failoverparameter is disabled.
- Refresh rate dropdown. The frequency with which the data is refreshed.
- Create a new MaxScale object button.
Settings
This page shows and allows editing of MaxScale parameters.
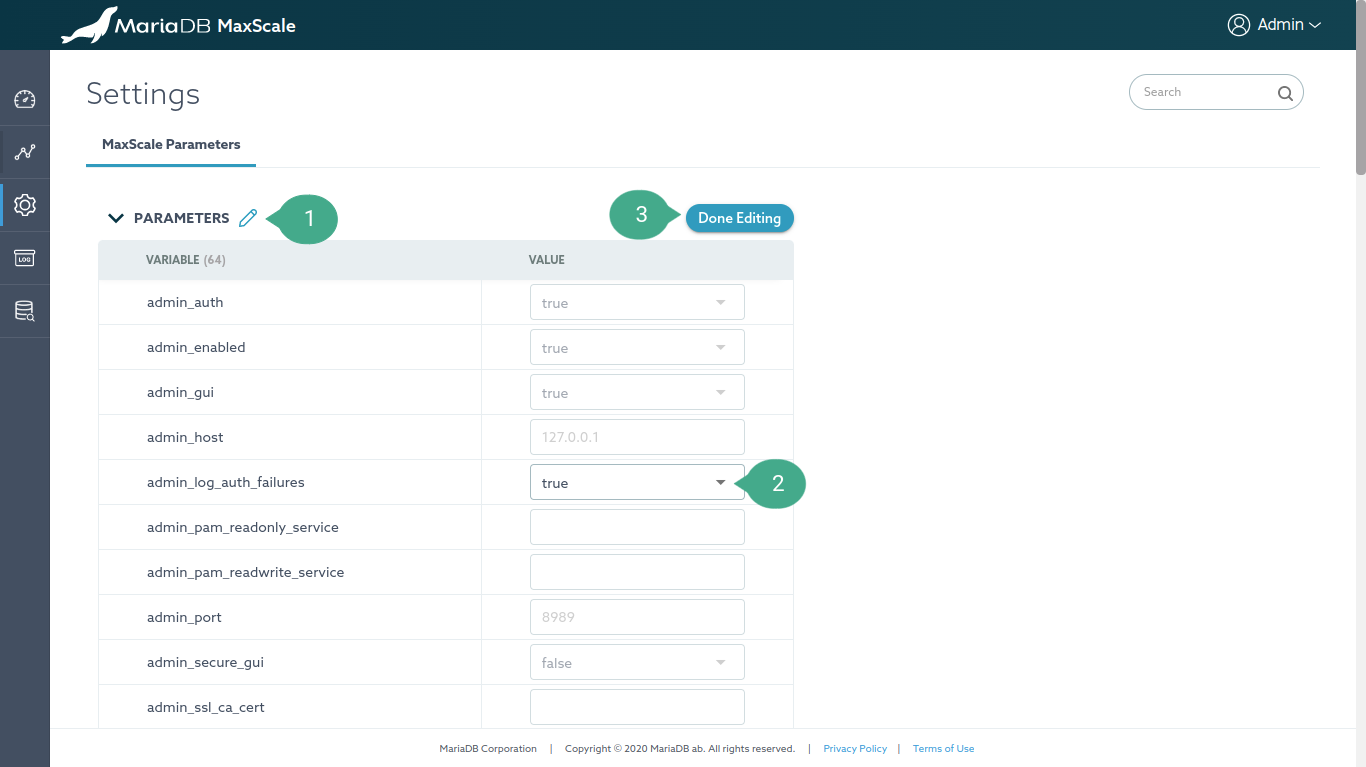
Annotation
- Edit parameters button. This button is shown on the mouseover event allowing to edit the MaxScale parameter. Clicking on it will enable editable mode on the table..
- Editable parameters are visible as it's illustrated in the screenshot.
- After finishing editing the parameters, simply click the Done Editing button.
Logs Archive
This page show real-time MaxScale logs with filter options.
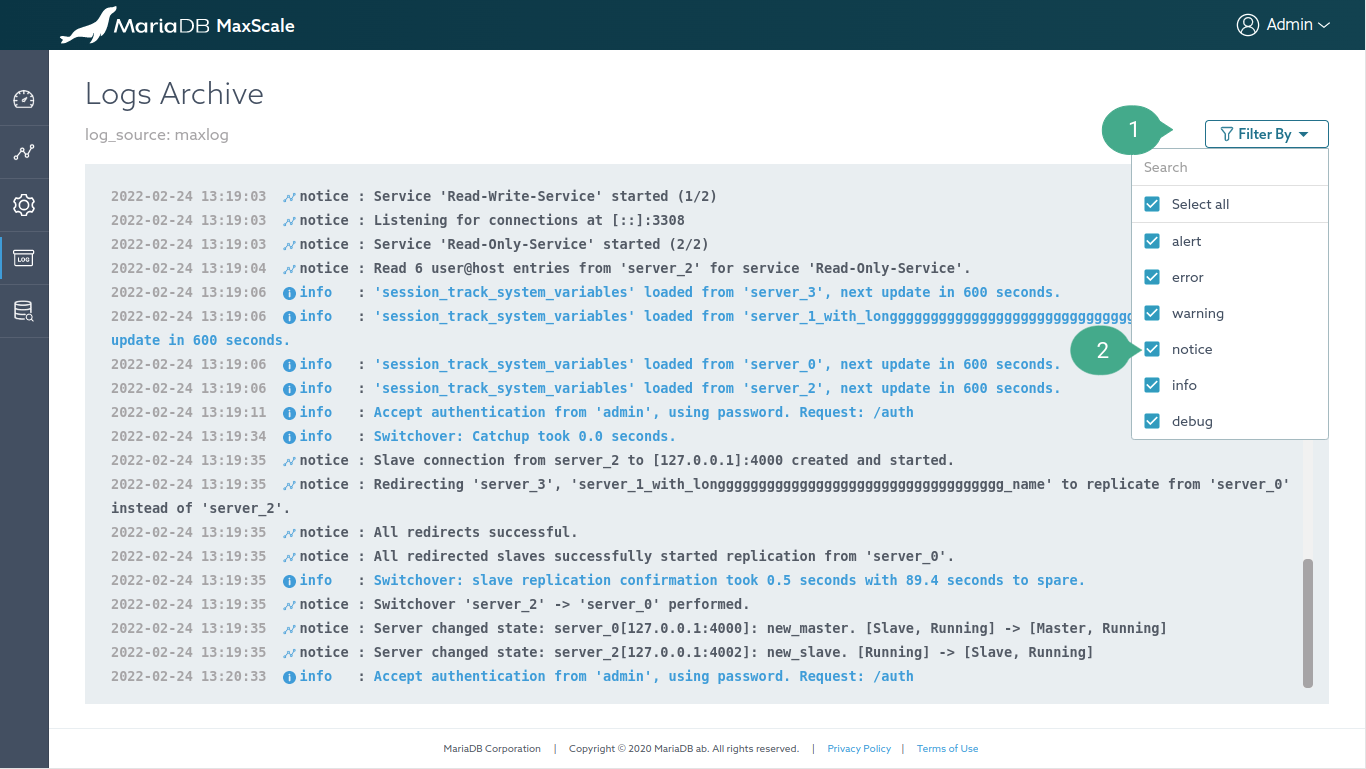
Annotation
- Filter by dropdown. All logs types are selected to be shown by default
- Uncheck the box to disable showing a particular log type.
Query Editor
A SQL editor tool to run queries and perform other SQL operations.
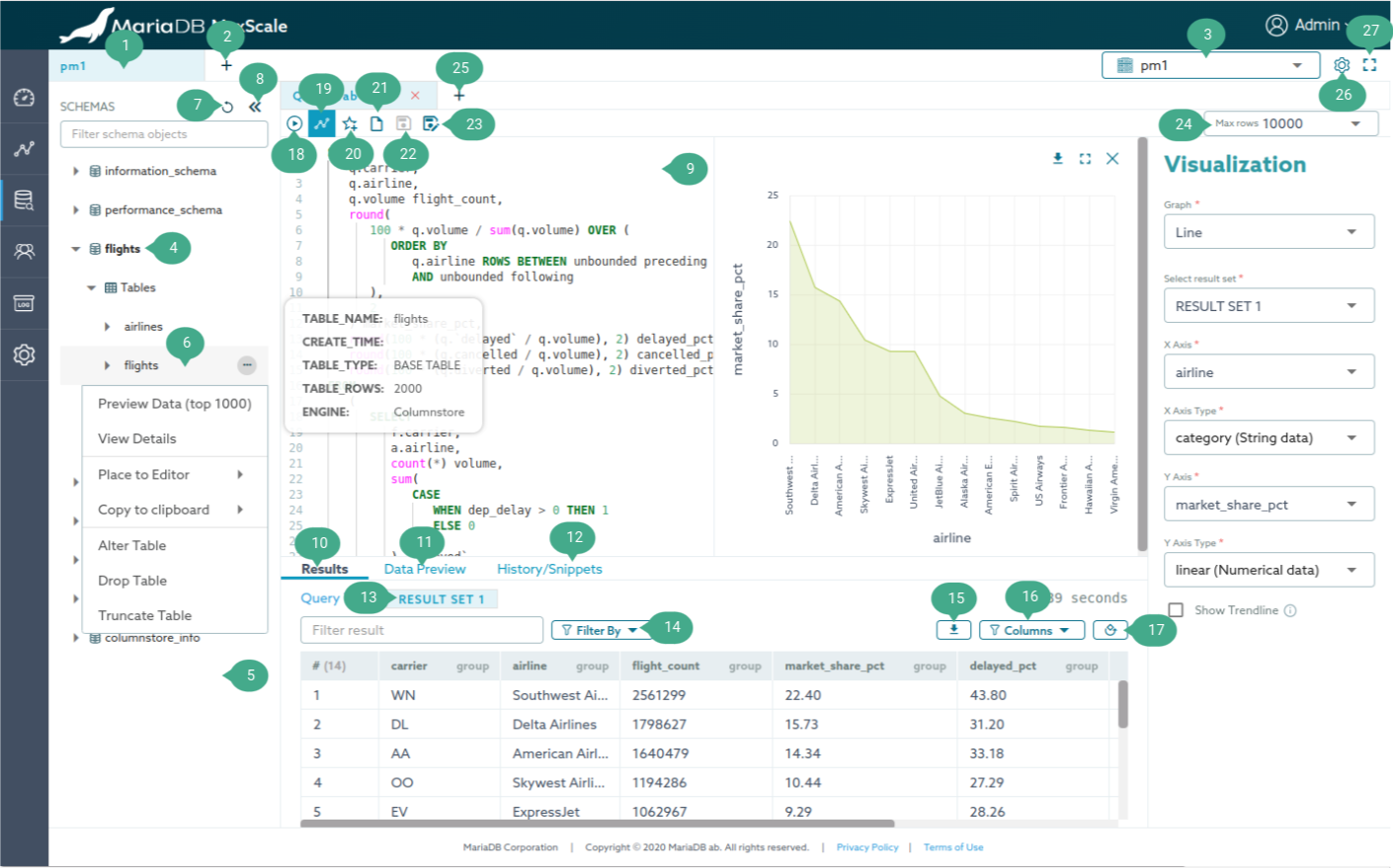
Annotation
- Worksheet tab navigation. Each worksheet is bound to a connection, so sessions querying within a worksheet is not yet supported.
- Add a new worksheet button.
- Connection manager dropdown. With this dropdown, you can create a new
connection or change the connection for the current active worksheet. A new
connection can be created by selecting the last option in the dropdown
labeled as
New connection. Once a connection is created, it automatically binds the connection to the current active worksheet. - Active database dropdown. Right-click on the database name and click
Use databaseoption to quickly change the default (current) database - Schemas sidebar. Showing available schemas on the current connection. As shown in the figure above, these items can be explored to show tables, stored procedures, columns, and triggers within the schema.
- Schemas sidebar object.
- Each object has its own context menu providing different options. e.g. For
the table object as shown in the figure above, it has options to
Preview Data (top 1000)andView Details. The query result for these options is shown in theData Previewresult tab which is annotated as number 12. The context menu can be shown by right-clicking on the object or clicking on the three dots icon placed on the right side of the object. - Quick access to the
Preview Data (top 1000)context menu option. For a table object, its preview data can also be seen by clicking on its name. - Quick overview tooltip. Each object has its own tooltip providing an overview of the object.
- Each object has its own context menu providing different options. e.g. For
the table object as shown in the figure above, it has options to
- Refresh schema objects button. After deleting or creating schema object, the
Schemas sidebarneeds to be manually refreshed. - Collapse the
Schemas sidebarbutton. - SQL editor. The editor is powered by
Monaco editor which means its
functionalities are similar to VS code. Available commands can be seen by
pressing F1 while the cursor is active on the editor. This is an intention
to prevent conflict between the browser's shortcut keys and the SQL
editor's. This also means the editor shortcut key commands are valid only
when the cursor is active on the
SQL editorwith an exception for theRun all statements,Run selected statementsandSave statements to favoritecommands. - Query Results. Showing the query results of queries written in the SQL editor.
- Data Preview. Showing the query results of
Preview Data (top 1000)andView Detailsoptions of the schema sidebar context menu. - History/Snippets. Showing query history and snippet queries.
- Result tab navigation. Navigating between SQL queries results.
- Filter query history logs. The query history is divided into two types of
logs The
User query logscontains logs for queries written in theSQL editorwhile theAction logscontains logs for auto-generated SQL, such asPreview Data (top 1000),View Details,Drop TableandTruncate Table. - Export query result button. Exporting as
json,csvwith a custom delimiter. - Filter query result columns dropdown. Selecting columns to be visible.
- Vertical query result button. Switching to vertical mode.
- Run button. Running the queries written in the
SQL editor. Alternatively, pressingCtrl/CMD+Shift+EntertoRun all statementsorCtrl/CMD+EntertoRun selected statements. - Visualize query result button. Visualizing a query result into a line, scatter, vertical bar, and horizontal bar graph.
- Create a query snippet from the queries written in the
SQL editor. Alternatively, pressCtrl/CMD+D. - Open Script button.
- Save Script button. This writes content into the opened file. This only works on Chrome or any browsers based on Chromium served over a secure connection (https)
- Save Script As button. Save the content as a new file.
- sql_select_limit input. Changing the maximum number of rows to return from SELECT statements.
- Add a new session button.
- Query Editor settings button. Open
Query configurationdialog to change the value ofMax rows(sql_select_limit),Query history retention period (in days),Show confirmation before executing the statementsandShow system schemas. - Maximize Query Editor window.
How to kill a session
A session can be killed easily on the "Current Sessions" table which can be found on the Dashboard, Server detail, and Service detail page.
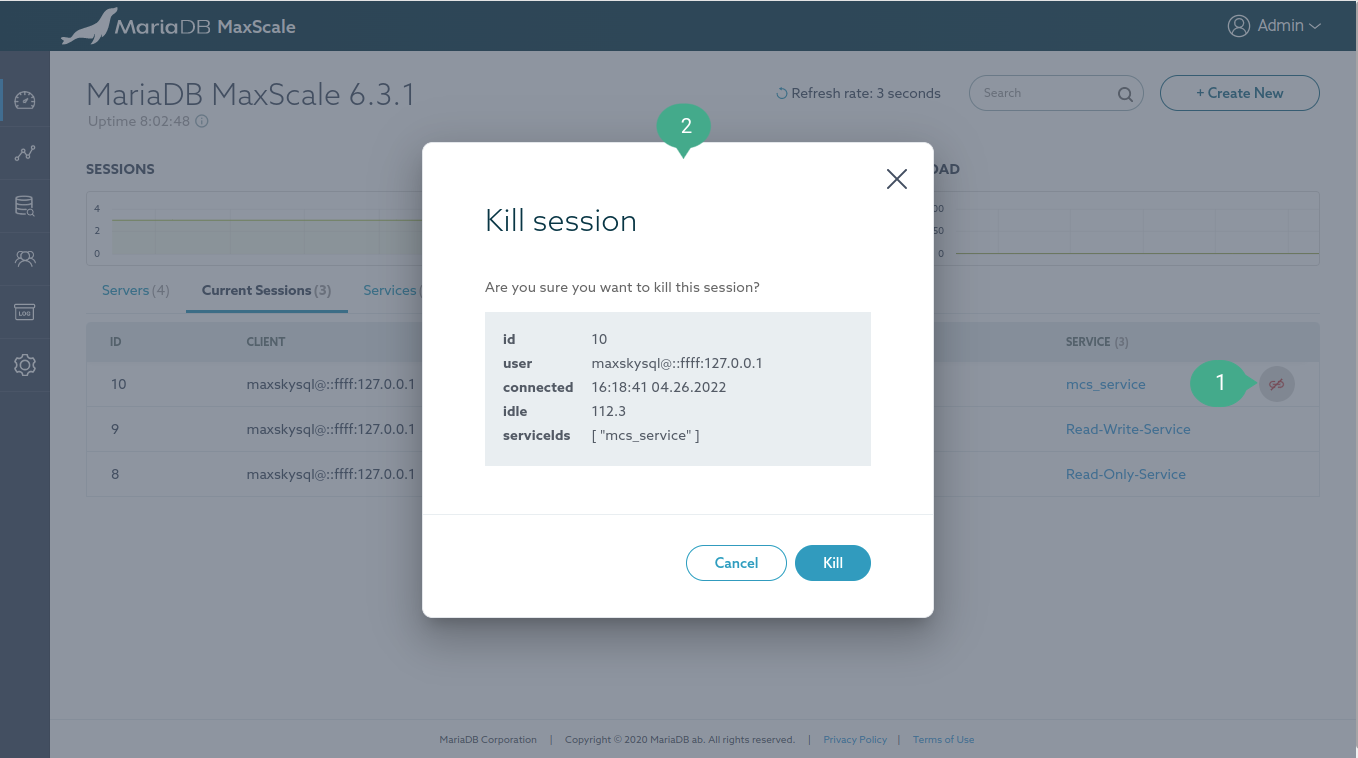
Annotation
- Kill session button. This button is shown on the mouseover event.
- Confirm killing the session dialog.

